Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
Calculation of Buffer Storage Tank
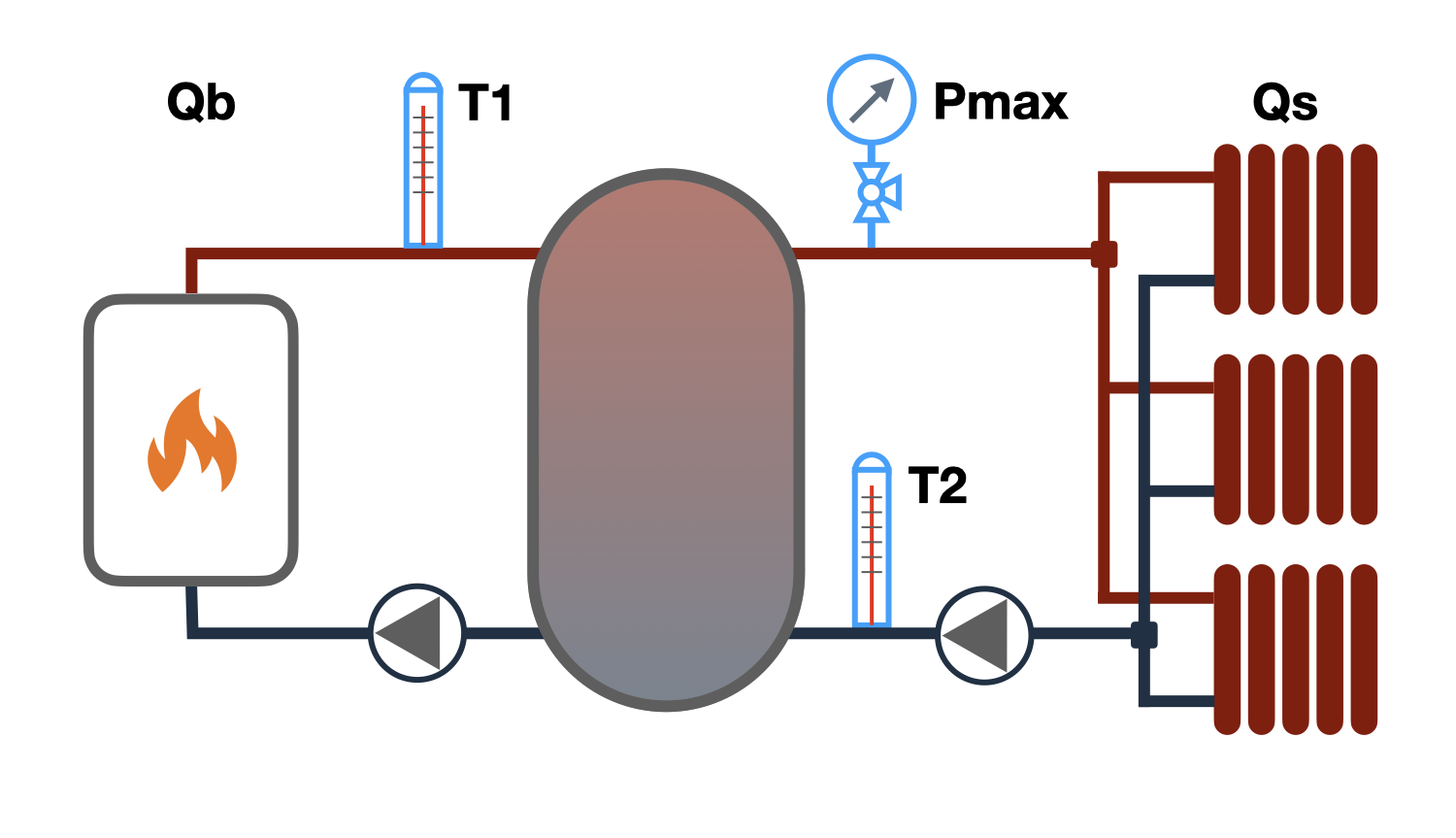
Selection of Buffer Storage Tank
The buffer storage tank is selected for a previously chosen heat source (boiler) and calculated in such a way that it can accumulate all the heat produced by this source, or for a consumer that should be provided with heat produced by a low-power source before the time of heat consumption.
The priority in selecting a buffer storage tank will be the source, if its power or heat generation time is limited, for example:
- In a scheme with a solid fuel boiler for accumulating heat from a one-time fuel load and subsequent analysis by the heating system during the day.
- In a solar collector with heat collection during daylight hours and peak or uniform use during the day in the hot water supply system.
The priority in selecting a buffer storage tank will be the consumer, if it is necessary to cover a given heat load in a certain time, for example:
- In heating systems in which the source of heat is an electric boiler that works only during the reduced night tariff.
- In hot water supply systems with a given high peak consumption of hot water and heating of this water by a low-power source during the day (such a scheme is used in baths).
Calculation of the Buffer Storage Tank
Calculation of the buffer storage tank consists of determining the accumulative capacity of the stored volume of water. The accumulative capacity of water is characterized by heat capacity equal to 4.187 kJ * kg/°C. This means that to heat one kilogram of water by 1°C, it is necessary to supply the amount of heat equivalent to 4.187 kJ or, which is also the same, = 1 kcal = 1.163 W. For example, if we have a buffer storage tank with a volume of 1000 liters (further on, the mass of 1 liter of water is assumed to be equal to 1 kg) and we heat it to 50°C, then it will accumulate heat energy 1000 * 50 = 50,000 kcal = 0.05 Gcal = 58 kWh. When removing heat and cooling the tank by 50°C, 0.05 Gcal of heat will be removed from it, respectively.
Depending on the application scheme, different methods of calculating buffer storage tanks are used, but in general, the following should be taken into account when choosing:
- The greater the peak heat consumption differs from the hourly average and the longer its duration, the larger the volume of the buffer storage tank should be.
- The greater the peak heat input and the shorter its duration, the greater the power of the heat exchanger should be, regardless of whether it is external or integrated into the buffer storage tank.
- The nominal pressure of the PN buffer storage tank must be greater than the maximum working pressure at the point of its connection.
- In buffer storage tanks with two or more heat exchangers - systems with a higher temperature are connected to the upper heat exchangers, and with a lower one - to the lower ones.
- The buffer storage tank connected to the solid fuel boiler must store the heat generated by at least one boiler loading.
- All schemes with buffer storage tanks must have an expansion tank and a safety valve
question : comment : feedback
 Online Equipment calculations
Online Equipment calculations























 EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE








