Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
Calculation and Selection of the Pressure Tank
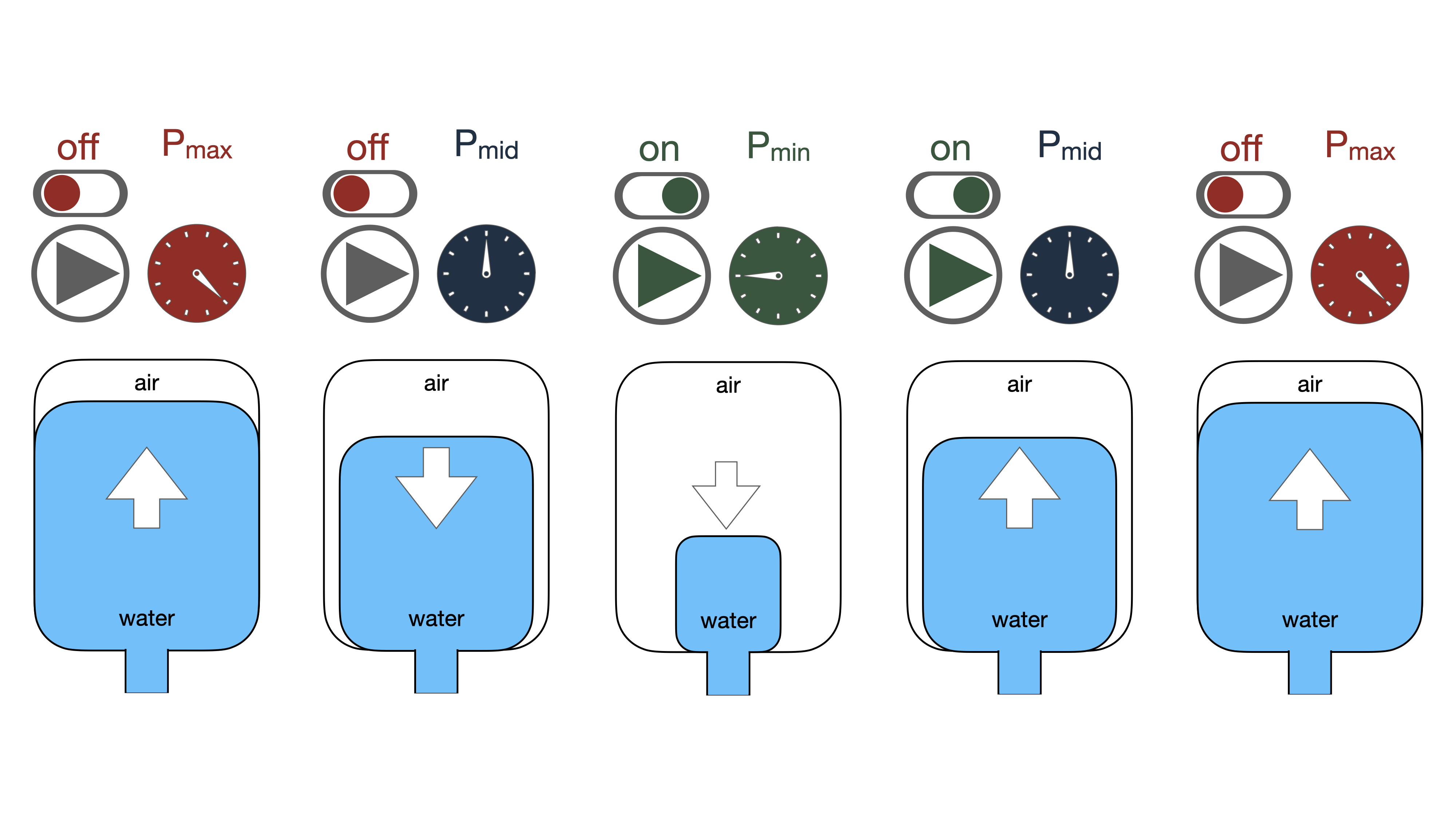
Pressure Tank Calculation
In water supply systems, pressure tanks solve many tasks, and calculations for each case are performed using different methodologies. The algorithm above allows you to select tanks for two of the most popular tasks and determine the initial gas space pressure, pump activation, and deactivation pressures.
The first calculation option for the pressure tank prioritizes pump activation frequency. In systems with booster stations, well pumps, and booster pumps, a pressure tank is required to reduce the frequency of pump activation.
Water cannot be compressed like air due to its physical properties. Therefore, even a short-term opening of one faucet in a multi-apartment building can cause the pump to turn on. Frequent pump activation leads to rapid wear and breakdown.
The activation frequency is related to the pump's electric power. For example, pumps with a power of more than 8 kW should be activated no more than 10 times per hour, pumps with a power of less than 5 kW – no more than 20 times per hour, and pumps in the range of 5 to 10 kW should be activated slightly more than 15 times per hour. This dependence is the basis of the calculation algorithm above.
In addition to pump power, many other factors influence the allowable activation frequency, such as the mass of moving parts. The larger the mass, the lower the allowable activation frequency. Therefore, pay attention to the match between the activation frequency values obtained from the pressure tank selection and the optimal frequency for the selected pump, and if necessary, recalculate the tank.
The second calculation option for the pressure tank prioritizes the stored water volume. It is recommended for systems where water supply interruptions are not allowed, but there are power outages or interruptions in the centralized water supply.
Pressure Tank Selection
The selected pressure tank volume should be equal to or greater than the volume obtained from the calculation. There are no negative consequences of oversizing the pressure tank, regardless of how much the volume exceeds the calculated value.
When selecting a pressure tank, consider its temperature and strength characteristics. The maximum tank pressure must be equal to or greater than the maximum pressure at the connection point.
If the installation of pressure tanks is planned indoors, keep in mind that tanks with a diameter larger than 750 mm and a height greater than 1.5 m may not fit through the doors, and mechanized means may be required for transportation. In this case, it is better to opt for several smaller pressure tanks instead of one large one.
When selecting a pressure tank, remember that the stored water volume in it is, on average, 40-50% of the tank's total volume.
Pressure Adjustment in the Pressure Tank
Before connecting to the water supply system, it is necessary to set the gas space pressure in the pressure tank Pg (inflate the tank) according to the value provided in the calculation results. To do this, it may be necessary to release pressure through the valve or inflate the tank with a compressor, depending on the factory-set gas space pressure. After setting the gas space pressure, connect the tank to the water supply system.
Adjust the pump control automation so that the pump activation and deactivation pressures match the calculated values.
The maximum water pressure Pmax is typically not more than 4.5 bar, and in some cases, 6 bar. As a minimum, Pmin is the pressure at which the excess pressure at the top faucet is the minimum allowable value, usually (0.2-1.0 bar).
question : comment : feedback
 Online Equipment calculations
Online Equipment calculations























 EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE








