Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
Technical characteristics of balancing valves
Kvs valve flow coefficient - the numerical value of the flow coefficient Kvs is equal to the water flow rate through the valve in m³/hr at a temperature of 20°C at which the pressure drop across it will be 1 bar.
Authority of the balancing valve - characterizes the regulating ability of the valve. The numerical value of the authority is equal to the ratio of the pressure drop across the fully open valve to the pressure drop across the regulated section.
The lower the authority of the balancing valve, the more its flow characteristic deviates from the ideal and the less smooth the flow rate changes during the stroke movement. For example, in a system where a valve with a linear flow characteristic and low authority is installed, closing the passage area by 50% can reduce the flow rate by only 10%, while with high authority, closing it by 50% should reduce the flow rate through the valve by 40-50%.
It is recommended to lose no less than 50% of the available head on a balancing valve with a linear characteristic, and no less than 10% on a valve with a logarithmic characteristic.
Flow characteristic of balancing valve shows the dependence of the relative flow rate change on the relative stroke change of the valve at a constant pressure drop on it.
Linear flow characteristic - equal increments of the relative stroke cause equal increments of the relative flow rate. Balancing valves with linear flow characteristic are used in systems where there is a direct dependence between the controlled variable and the flow rate of the medium, for example, in nodes for mixing the heat carrier.
Equal percentage flow characteristic (logarithmic) - the dependence of the relative increase in flow rate on the relative increase in stroke is logarithmic. Balancing valves with a logarithmic flow characteristic are used in systems where the controlled variable is nonlinearly dependent on the flow rate. They are ideal for regulating heat transfer in high-speed heat exchangers and heating devices, as well as in systems with low authority of the regulating valve.
Parabolic flow characteristic - the dependence of the relative increase in flow rate on the relative stroke change follows the quadratic law (goes through a parabola). Balancing valves with a parabolic flow characteristic are used as a compromise between valves with linear and equal percentage characteristics.
Kvs flow coefficient of balancing valve - the numerical value of the Kvs flow coefficient is equal to the water flow through the valve in m³/h at a temperature of 20°C, at which the pressure drop on it will be 1 bar.
Authority of balancing valve - characterizes the regulating ability of the valve. The numerical value of the authority is equal to the ratio of the pressure drop on the fully open valve to the pressure drop on the regulated section.
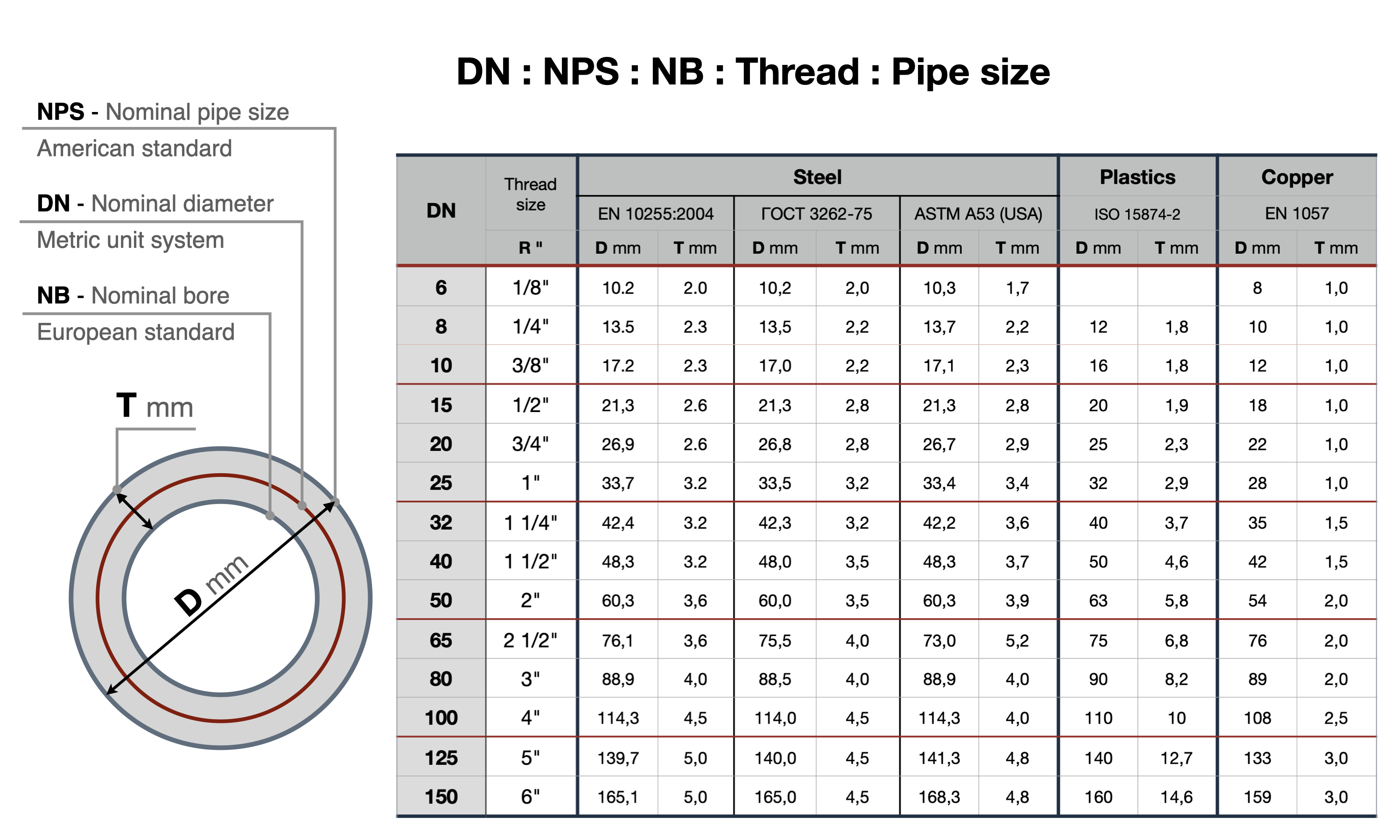
DN of balancing valve - nominal diameter of the connecting pipes. DN values are used to standardize the sizes of pipeline fittings. The actual diameter of the opening may differ slightly in either direction from the nominal.
PN of balancing valve - nominal pressure is the maximum excess pressure of the working medium at a temperature of 20°C, at which long and safe operation is ensured.
question : comment : feedback
420
 Catalog of
Catalog of balancing valves
Herz
Herz
Herz
Herz
Herz
Herz
Herz
Herz
Zetkama
Zetkama
Danfoss
Danfoss
Danfoss
Danfoss
Danfoss
Honeywell - Resideo
Honeywell - Resideo
Honeywell - Resideo
Honeywell - Resideo
ARI Armaturen
ARI Armaturen
Oventrop
Oventrop
Oventrop
IMI Hydronic
IMI Hydronic
IMI Hydronic
IMI Hydronic
IMI Hydronic
IMI Hydronic
VIR
VIR
VIR
Frese
Vexve
Vexve
Danfoss
Danfoss
IMI Hydronic
IMI Hydronic
IMI Hydronic
IMI Hydronic
Zetkama
Zetkama
VIR
Comap
Comap
Comap
Herz
Vexve
Vexve
Broen
Broen
Broen
Broen
Broen
Broen









 EN 1092-1
EN 1092-1
