Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
Technical specifications of the safety valve
Setting Pressure of Safety Valve - the maximum overpressure at the inlet of the valve, at which the valve disc is closed and provides the specified tightness of the closure.
Start-to-Discharge Pressure (blowdown, set pressure) - the pressure at which the valve disc bursts and a slight release of the medium occurs. In most safety valves, the start-to-discharge pressure is approximately 3% higher than the setting pressure.
Full Lift Pressure - the minimum pressure at the inlet of the safety valve, at which the valve closure reaches its maximum lift. In two-position safety valves, the full lift pressure equals the start-to-discharge pressure. In proportional action valves, the full lift pressure exceeds the start-to-discharge pressure by approximately 10%.
Closing Pressure (seating or reverse seating) - the maximum pressure at which the valve closure seats fully on the seat and provides a tight shut-off of the flow. In proportional action safety valves, the closing pressure is 10-20% lower than the setting pressure, due to the additional overcoming of the dynamic pressure of the passing medium.
Design Pressure (maximum allowable pressure) - the excess pressure on which the strength of the equipment or vessel is calculated, or the maximum pressure set by the equipment manufacturer. The full lift pressure of the safety valve should not exceed the design pressure.
Flow Capacity of Safety Valve - the flow rate of the working medium discharged by the valve at specific inlet and outlet pressures, a certain temperature of the working medium, and a certain stroke of the valve stem.
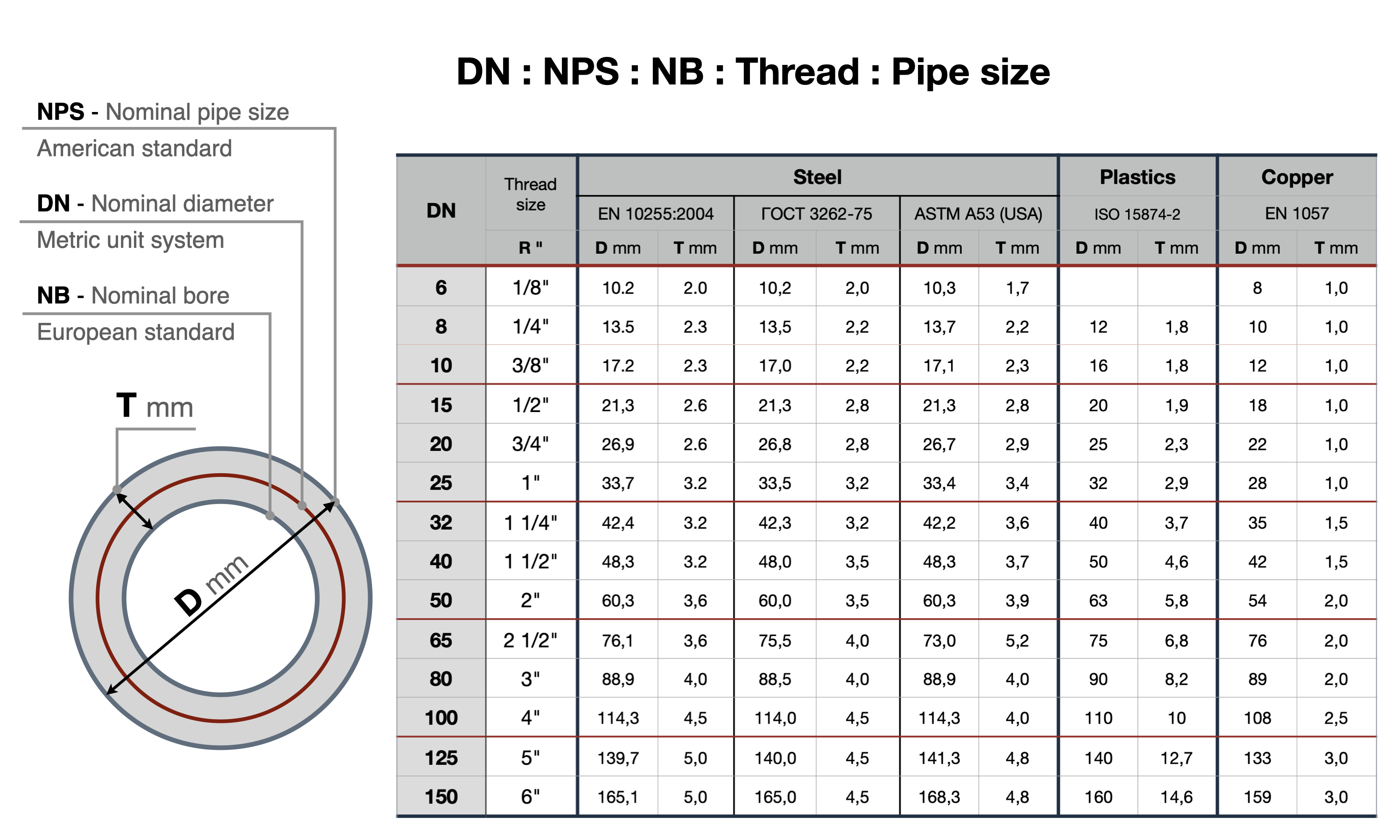
DN of Safety Valve - the nominal diameter of the opening in the connecting flanges. The DN value is used to standardize the dimensions of pipeline fittings. The actual diameter of the opening may differ slightly in either direction.
question : comment : feedback
423
 Catalog of
Catalog of safety valves
Valtec RUS
Watts
ARI Armaturen
Afriso
Afriso
Afriso
Swagelok
Flamco
Flamco
Pneumatex
Pneumatex
Pneumatex
Duco
SYR
SYR
Officine Rigamonti
Zetkama
Zetkama
TLV
TLV
LDM
LDM
Honeywell - Resideo
Honeywell - Resideo
Danfoss
Danfoss
Danfoss
IMI Hydronic
IMI Hydronic
IVR
Samson
Valtec RUS
Armak
Genebre








 EN 1092-1
EN 1092-1
