Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
Design of buffer storage tank
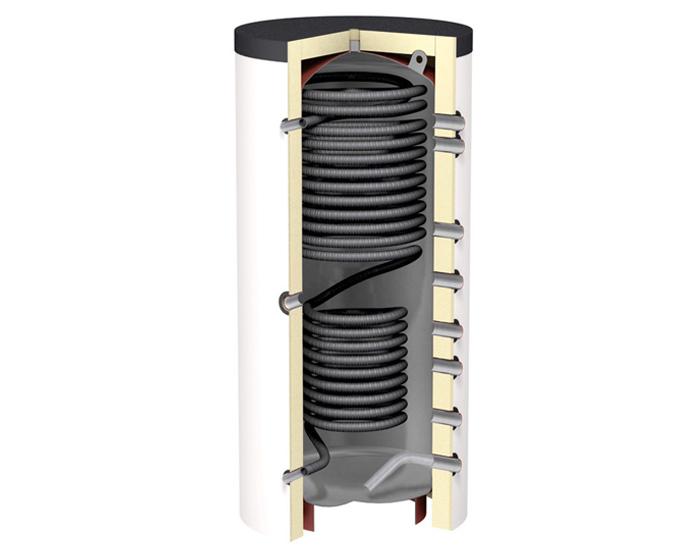
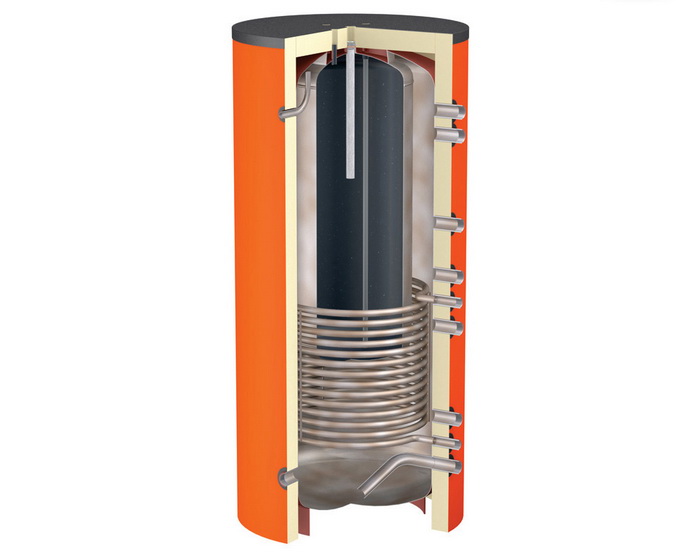
The construction of a buffer storage tank is a steel, sealed, and thermally insulated tank with connections for a heat source and consumer. Depending on the usage conditions, a buffer storage tank can contain the following elements:
- A heat exchanger in the lower part of the tank
- An integrated tank for the hot water supply system
- An integrated heat exchanger for the hot water supply system
- A magnesium anode
- An electric heater
- A device for layer-by-layer heating
Since several heat sources and consumers can be connected to a single buffer storage tank, the number of connections in its design can vary.
Buffer storage tanks without a heat exchanger, with direct connection of the consumer without additional mixing devices and heat exchangers, are used if:
- The quality requirements of the heat carrier in the heat source and consumer circuit are the same.
- The working pressure in the heat consumer (at all modes) does not exceed the maximum allowable pressure for the heat source and the buffer storage tank itself.
- The working temperature of the heat carrier (at all modes) at the heat source outlet does not exceed the maximum allowable temperature for the consumer.
If the working pressure in the heat consumer circuit exceeds the allowable pressure for the source or the buffer storage tank at any of the modes, the connection of the consumer should be made in a closed circuit through a heat exchanger.
If the temperature in the heat source circuit may exceed the allowable temperature for the consumer at any of the modes, or if the consumer has a quality regulation, the connection of the consumer is made through a mixing unit with a three-way valve.
Buffer storage tanks with a heat exchanger at the bottom are used if:
- The pressure or temperature in the heat source circuit exceeds the allowable values for the consumer and the buffer storage tank itself.
- There are different quality requirements for the heat carrier in the heat source and consumer circuits.
- An additional heat source, such as a solar collector or heat pump (bivalent system), needs to be connected.
A spiral heat exchanger made of smooth or corrugated stainless steel tubes is usually used as the heat exchanger. To perform maintenance of the heat exchanger, a revision flange is provided in the construction of the buffer storage tank.
In such buffer storage tanks, water is constantly circulating, being heated at the bottom and rising upward, while cooler water moves downward.
If the determining condition is different working parameters of the working medium in the heat source and consumer circuits, the heat source circuit is connected to the heat exchanger located at the bottom.
In bivalent systems with two or more heat sources, the source with lower water heating temperature, such as a solar collector or heat pump, is connected to the heat exchanger located at the bottom of the tank.
Buffer storage tanks with an integrated tank are used when connecting a hot water supply system to a heat source whose heat production peaks do not coincide with the hot water consumption peaks.
The integrated tank, filled with sanitary water, is heated by the heat carrier that comes to the buffer storage tank from the heat source and, when it is turned off, keeps the water hot until it is used.
Buffer storage tanks with integrated tanks are installed in hot water supply systems with short-term water consumption peaks due to their low power duration of heating, compared to spiral heat exchangers.
The tanks integrated into the buffer storage tanks are covered with enamel suitable for sanitary water or made of stainless steel.
Heat accumulator tanks with a built-in heat exchanger for hot water supply systems are used in cases where there are no pronounced peaks of water consumption, but there is a need for high long-term heating power.
The water that enters the HWS system is heated in the tubular space of the spiral heat exchanger, which is mainly located in the upper part of the tank, with the water inlet located at the bottom and the outlet at the top tube.
The smooth or corrugated tube of the built-in heat exchanger is made of stainless steel suitable for contact with drinking water.
The versatility of possible heat accumulator schemes has led to many modified designs with combined use of several devices described above.
In heat accumulator tank constructions for systems with high water corrosion activity, a magnesium anode is provided to ensure electrochemical cathodic protection of the tank body.
Additional water heating is provided by an electric heater, which can raise the water temperature to the desired level in case of insufficient temperature of the water coming from the source or during the absence of heat flows from the heat source.
To reduce the intensity of water mixing in the heat accumulator tank construction, a layered heating device is added, which allows to significantly increase the efficiency of low-temperature heat sources, such as a heat pump.
The thickness of the thermal insulation of the heat accumulator tank determines the amount of heat loss and the rate of cooling, so in systems with a need for long-term storage of accumulated heat, it is recommended to choose a thicker thermal insulation structure.
P.S. The heat accumulator tank is designed for storing hot technical water, and the water for water supply systems can be heated in the built-in heat exchanger or tank. Tanks designed for heating and storing sanitary-technical water are presented in the section of our catalog - Water heater tanks.
question : comment : feedback
327
 Catalog of
Catalog of Buffer storage tanks
Viessmann
Viessmann
Viessmann
Viessmann
Viessmann
Elbi
Теплобак
Теплобак
Теплобак
Теплобак
Wolf
Wolf
Wolf
Huch
Huch
Zani
Zani
Zani
Flamco
Flamco
Flamco
Flamco
Reflex
Reflex
Reflex
Rehau
Bosch
Bosch
Huch
Vaillant
Vaillant
Zani