Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
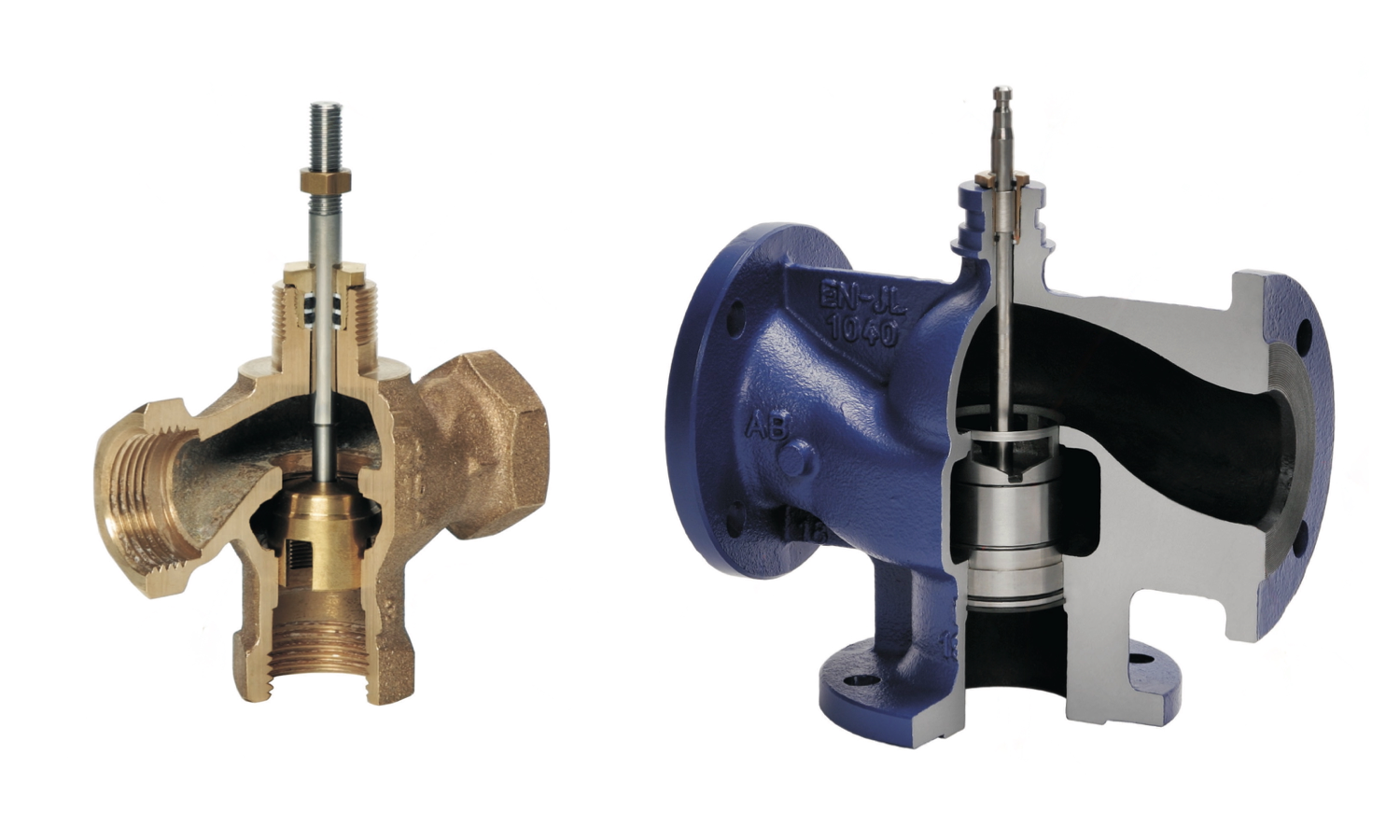
The construction of a three-way valve
Three-way valve construction - a valve is fixed on a stem that moves linearly (up/down) and in the extreme upper position closes port A while fully opening port B, and in the extreme lower position closes port B while fully opening port A. Regardless of the stem position, the heat carrier flow through port AB remains constant (provided the valve is properly selected).
Seat-type three-way valves are controlled by linear electric actuators with stem movement. When selecting a control valve actuator, it should be noted that in most seat-type valves, when the stem is moved downward, the direct path (A) is opened and the bypass path (B) is closed.
The valve structure of a seat-type valve depends on the necessary regulation law for each stroke and for what purpose the valve is intended - for separation or mixing of the flow.
Ports B and A in seat-type valves can have different configurations of the valve-seat pair, allowing for different control characteristics for each port depending on the needs of the controlled object.
Compared to a rotary valve, a seat-type three-way valve provides higher regulation accuracy, greater flow shutoff density, and can operate at high temperatures and pressure drops of the controlled flow, but its cost is significantly higher.
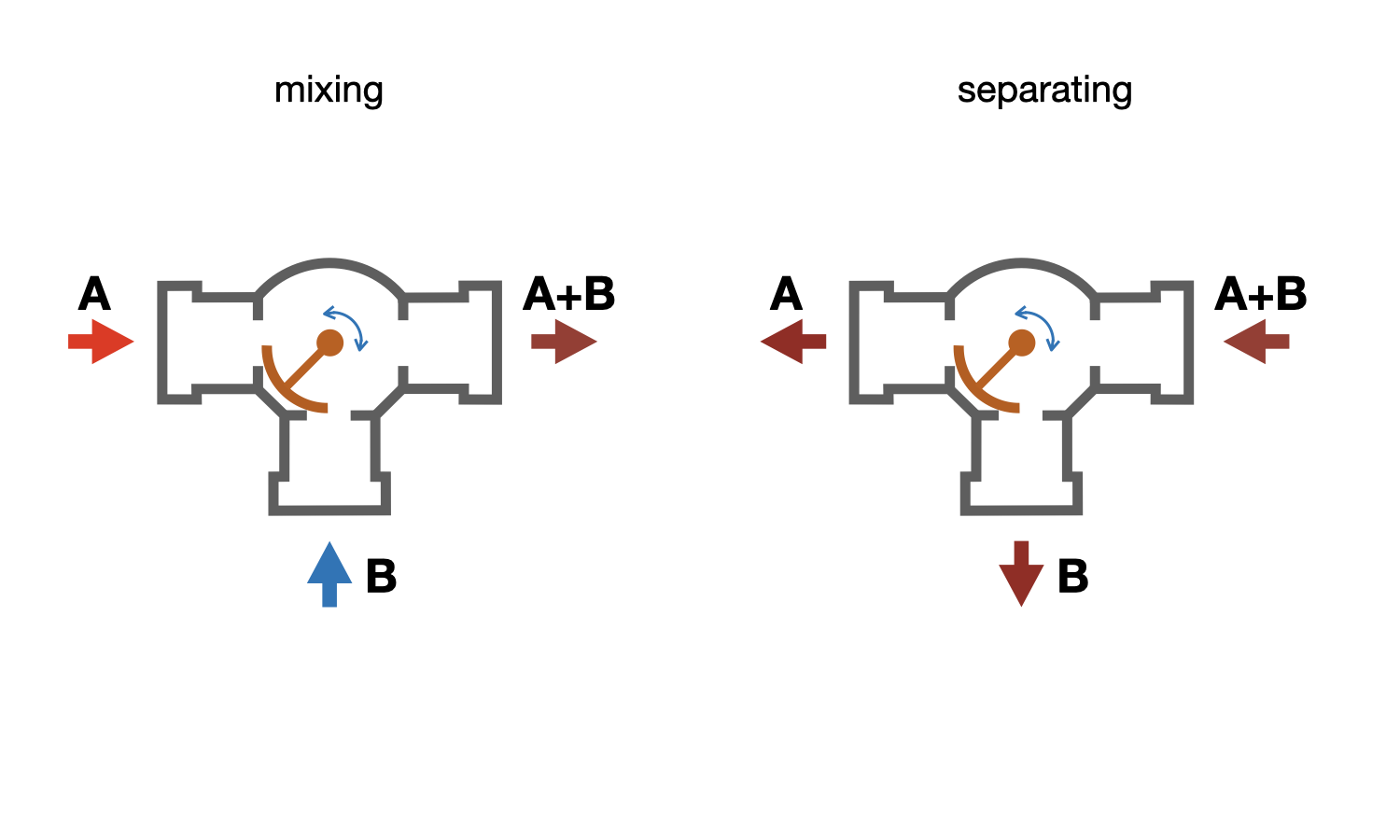
Rotary three-way valve construction - a valve is fixed on a radially rotatable stem with a 90-degree rotation angle, closing port B in the extreme left position and port A in the extreme right position. Regardless of the stem position, the heat carrier flow through port AB remains constant (provided the valve is properly selected).
Rotary three-way valves are controlled by rotary actuators with a radially rotating stem.
The three-way valve construction includes three ports (strokes):
- 1. Direct stroke, denoted by the letter - A - water flow can vary within the range from zero to maximum (AB) - the port can be completely closed;
- 2. Bypass stroke (perpendicular), denoted by the letter - B - water flow can vary within the range from zero to maximum (AB) - the port can be completely closed;
- 3. Common inlet/outlet, denoted by the letters - AB - water flow depends on the authority of the valve, but the port cannot be completely closed.
Flanged three-way valves and threaded valves are produced depending on the type of connection to the pipeline. For pipelines with a nominal passage diameter of up to 65 mm, a working pressure of up to 16 bar, and a temperature of up to 130°C, threaded connection valves are usually installed, and in other cases - flanged connection valves.
question : comment : feedback
434








 Tutorial Belimo
Tutorial Belimo Catalog of
Catalog of 
