Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
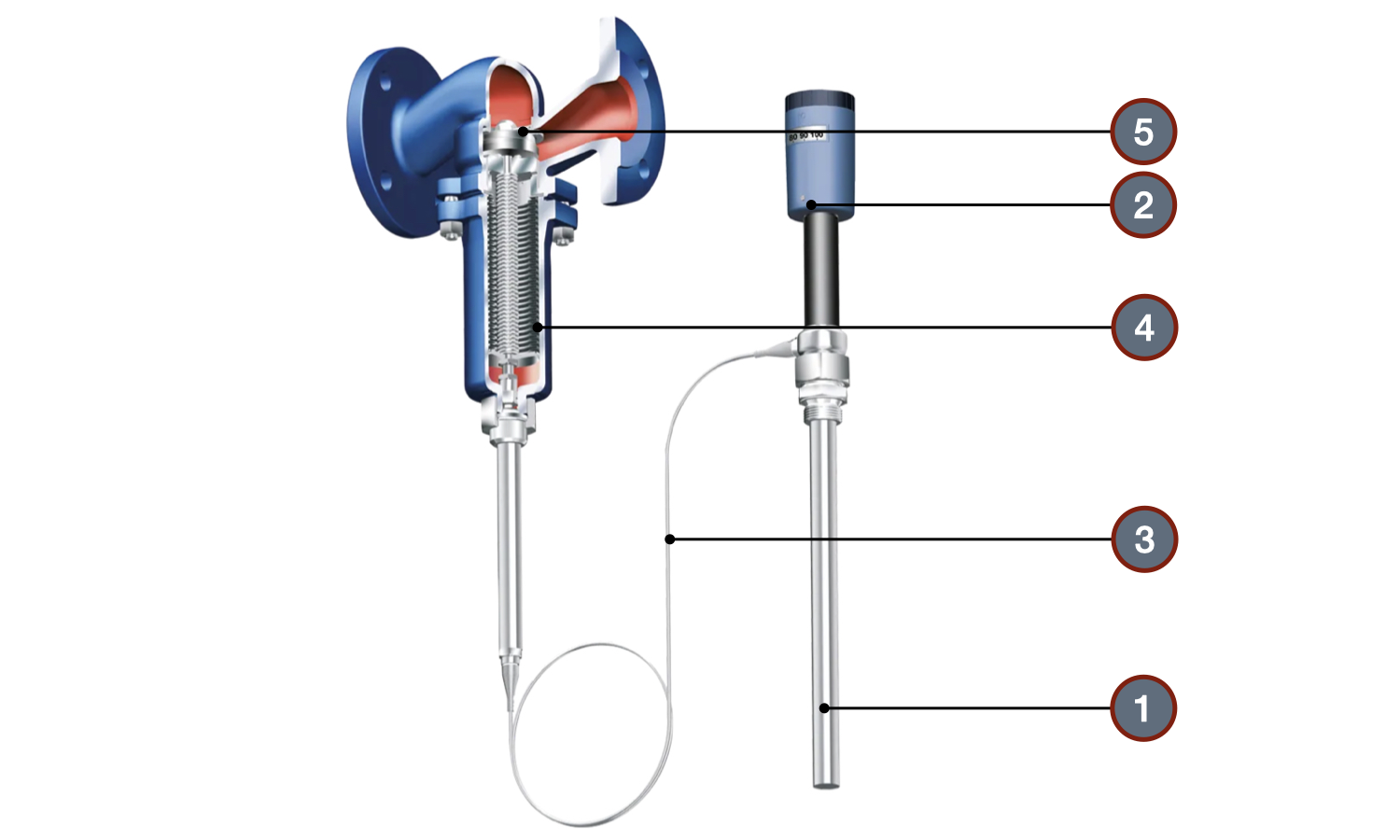
Construction of a direct-acting temperature regulator
- 1 - Temperature sensor
- 2 - Temperature adjustment handle
- 3 - Impulse tube
- 4 - Bellows pressing on the valve stem
- 5 - Valve shut-off element blocking the flow
The design of a direct-acting temperature regulator includes three components: a temperature sensor with an impulse tube, a thermoelement, and a regulating valve that can be connected either detachably or non-detachably.
Temperature sensor
The temperature sensor's design is a metal bulb filled with a working medium that significantly changes its volume when heated and connected to a thermostatic drive with an impulse tube. Regulators can be equipped with surface-mounted, immersion, or integrated temperature sensors.
Surface-mounted temperature sensors are attached to the surface of the pipe, easy to install, do not introduce additional hydraulic resistance, and do not require the use of special expanders. However, surface-mounted temperature sensors have high inertia and noticeable errors, which can be corrected by additional on-site adjustment.
Immersion temperature sensors are inserted into the pipeline through a protective sleeve or without it. They have significantly lower inertia but require welding work to install in the pipeline, introduce additional hydraulic resistance, and require expanders when installed on pipelines less than DN65.
Integrated temperature sensors are built into the temperature regulator's housing. Such regulators are used in schemes where it is necessary to maintain the temperature of water in the pipeline on which the regulating valve is installed according to the technological process, and the temperature of the heat carrier depends on its flow rate.
Thermostatic element
The design of the thermostatic element is a bellow connected to the temperature sensor with an impulse tube and filled with the same working medium as the temperature sensor.
The rigidity of the bellow's design allows it to expand with an increase in temperature and pressure of the working medium and move the stem of the regulating valve.
Regulating valve
The design of the direct-acting temperature regulator's valve does not differ from the valves used with other types of drives. Usually, it is a linear single-seat valve relieved by pressure, with a cast iron, steel, bronze, or brass body, which is connected to the pipeline with flanges, threads, or ends for welding.
question : comment : feedback
189
 Catalog of
Catalog of temperature controllers
Danfoss
Danfoss
Danfoss
Danfoss
Danfoss
ARI Armaturen
ARI Armaturen
ARI Armaturen
ARI Armaturen
LDM
Termen
Termen
Samson
Samson
Samson
Samson
Samson








 Tutorial Herz
Tutorial Herz
