Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
Chemical cleaning of plate heat exchanger
Deposits on the plates of a heat exchanger, formed during operation, increase the thermal conductivity of the plates and reduce the cross-sectional area of the flow channels of the working fluid. The degree of contamination of the heat exchanger is judged by the increased hydraulic resistance and decreased thermodynamic characteristics.
Types of contamination of plate heat exchangers:
- Calcium and magnesium carbonate salts, sulfate salts that precipitate out - are removed by chemical cleaning;
- Damage to plates by corrosion caused by the aggressiveness of the working environment towards the plate material - a complex type of contamination for dissolution by chemical reagents and can only be guaranteed to be removed by disassembly cleaning;
- Sludge that passed through mesh filters - the method of removal depends on the nature of the sludge.
The contaminated heat exchangers are cleaned by the method of hydrochemical cleaning or disassembly cleaning. The recommended cleaning frequency is once every 2-4 years, depending on the quality of the working environment.
Hydrochemical cleaning
Hydrochemical cleaning is carried out using acidic solutions with a neutral effect on the surface of the plates and sealing elastomers. Chemical cleaning is effective for mildly polluted heat exchangers and allows up to 85% of the plate surface to be cleaned, which is usually sufficient for restoring acceptable operating conditions of the apparatus.
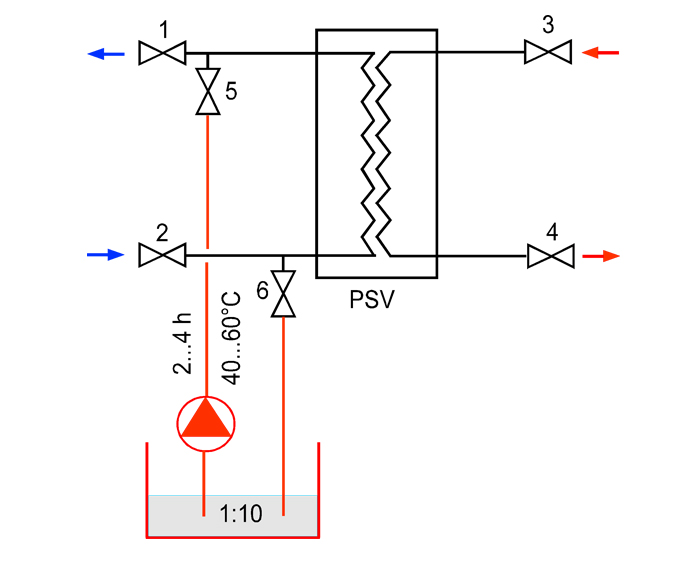
Diagram of the heat exchanger hydrochemical cleaning installation
The cleaning is performed through drain nozzles without disassembling the plate heat exchanger and disconnecting the connecting pipelines. The cleaning unit consists of a circulation pump and a buffer tank for preparing and collecting the acidic solution. Some modifications are additionally equipped with an electric heating element.
Each circuit of the plate heat exchanger is sequentially washed with a solution heated to 40-60°C for 2-4 hours, depending on the degree of contamination of the apparatus. The solution can be heated directly in the heat exchanger by starting the heating heat transfer medium in the adjacent circuit to be cleaned.
After hydrochemical cleaning of the heat exchanger cavity, it is necessary to flush it with clean water until the pH level at the outlet of the apparatus is fully equalized.
Reagents for chemical cleaning:
- A solution of hydrochloric and sulfuric acid - effectively copes with carbonate deposits (scaling), but due to the low pH level of 1, it can negatively affect the material of the plates. The aggressiveness of the reagents towards the plate metal is reduced by adding passivators and corrosion inhibitors to the acid solution.
- A solution of organic citric acid - less effectively dissolves carbonates, but is more loyal to the plate material.
- A solution of sulfaminic acid - dissolves scale and has significantly less corrosion activity than hydrochloric and sulfuric acids. When in contact with metal oxides, sulfaminic acid forms salts (sulfamates). Compounds containing fluorine are sometimes added to the solution to remove sulfates.
It is not recommended to perform flushing with:
- Additives containing chlorine;
- Nitric acid solution with a concentration greater than 0.5% (may damage sealing gaskets).
Safety measures
Chemical reaction occurs with the release of hydrogen, which together with oxygen forms an explosive mixture - periodically release oxygen that has entered the heat exchanger and has accumulated there during the flushing process.
A team of at least two people equipped with protective equipment that prevents acid from getting into their eyes and on their skin is allowed for the chemical flushing of the heat exchanger.
The used chemical reagent must be neutralized using special additives before being discharged into the sewage system.
question : comment : feedback
345
 Catalog of
Catalog of plate heat exchangers
Tranter
Alfa Laval
Funke
Sondex
Тепло-Поліс
Анкор-Теплоенерго
SWEP
Термопром









 Tutorial Danfoss
Tutorial Danfoss
