Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
How a three-way valve works
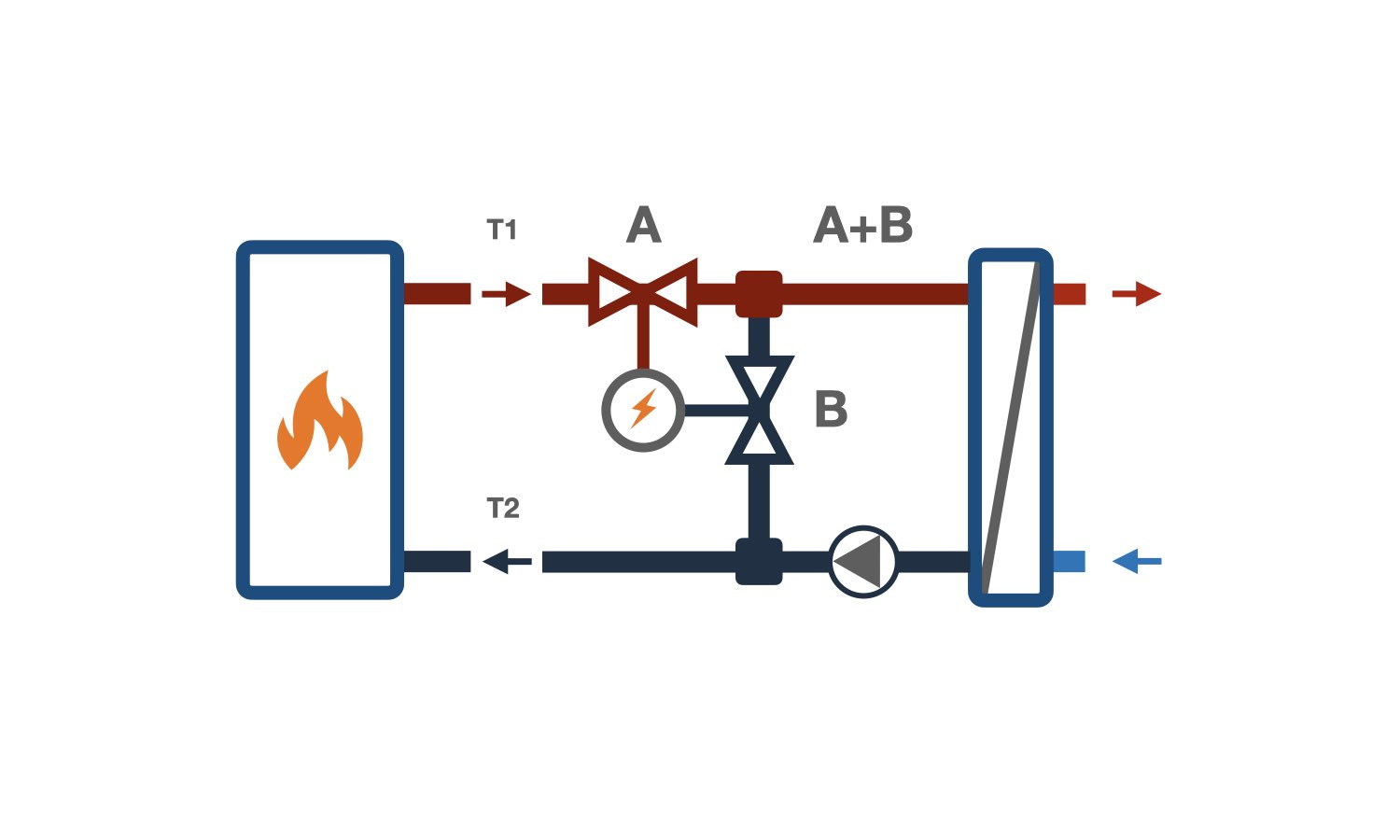
Three-way valve is designed to divide a circulation loop into a constant hydraulic mode loop and a variable hydraulic mode loop. Consumers requiring quality control are connected to the branch with constant hydraulic mode, while consumers with quantity control are connected to the branches with variable mode. In the quality control loop [AB], the three-way valve affects the mixing temperature [°C], but does not affect the flow rate [m³/h]. In the quantity control loop [A, B], the three-way valve changes the water flow rate [m³/h] and does not affect its temperature [°C].
The main difference between the operation of three-way valves and two-way valves is that, in any stem position, the water flow through the constant hydraulic mode branch [AB] remains almost unchanged — the valve cannot shut off the heat carrier supply. The constant hydraulic mode branch is marked AB on diagrams, while the variable mode branches are marked A and B.
The three-way valve operates together with an actuator. Typically, electric actuators are used, but thermostatic, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuators can also be used to control the valve. The choice of actuator depends on the technological process and the task the valve is intended to perform.
Thermostatic actuators are used in systems where the process requires maintaining a constant water temperature (e.g. in domestic hot water supply systems). Hydraulic and pneumatic actuators are used in complex technological installations and industrial applications.
The most common type is electric actuators with a linear stem movement, used with seat-type three-way valves. Such control systems are applied in heating systems where it is necessary to maintain different water temperatures going to heating devices depending on outdoor temperature changes. Additionally, electric actuators are used in centralized hot water heating systems and centralized cooling systems.
During operation, the valve shutter can be in one of the extreme positions — with branch [A] or [B] completely closed — or in an intermediate position with partially opened branches.
If the power supply to the electric actuator is lost, the valve may remain in its last working position or move the stem to the upper or lower position. The valve's behavior during power failure depends on the selected actuator.
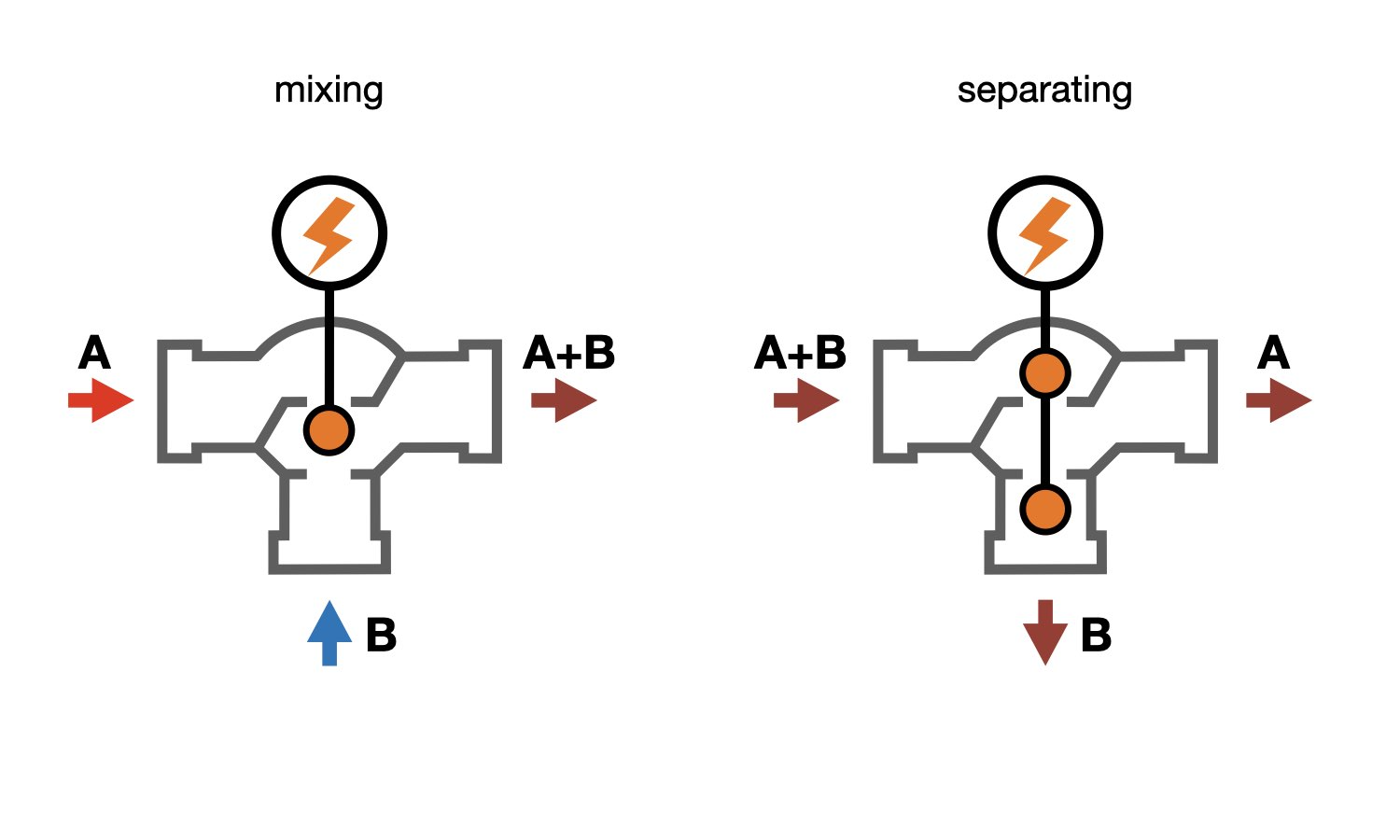
To simplify understanding of how a three-way valve works, it can be replaced with two two-way valves operating in reverse mode — opening one causes the other to close. The diagram shows a mixing three-way valve replaced by two two-way valves.
All three-way valves are divided by operation principle into those that mix two flows and those that divert the flow.
Mixing three-way valve — has two inlets and one outlet. It is used for quality control in heating systems by mixing two heat carrier flows with different temperatures. Quality control with maintenance of the set outlet temperature at port AB is achieved by changing the proportion between heat carriers with different temperatures coming from ports A and B. Some types of mixing three-way valves, when properly installed, can also perform flow diverting.
Diverting three-way valve — has one inlet and two outlets. It is typically used for quantity control by distributing the heat carrier flow in hot water systems and in piping nodes for air heaters and coolers. The inlet of a diverting valve is marked AB, and the outlets — A and B.
question : comment : feedback
515






 Basic schemes De Deitrich
Basic schemes De Deitrich Catalog of
Catalog of 
