Por favor, no bloquees los anuncios en nuestro sitio web. Los clics en los anuncios nos ayudan a existir, crecer y ser más útiles para ti.
Limpieza química del intercambiador de calor de placas
La incrustación en las placas del intercambiador de calor que se forma durante el uso aumenta la conductividad térmica de las placas y reduce el área de paso de los canales del medio de trabajo. El grado de contaminación del intercambiador de calor se evalúa por el aumento de la resistencia hidráulica y la disminución de las características termodinámicas.
Tipos de contaminación de los intercambiadores de calor de placas:
- sales de carbonato de calcio y magnesio, sales de sulfato que precipitan – se eliminan mediante limpieza química;
- daños en las placas por corrosión causados por la agresividad del medio de trabajo hacia el material de las placas – es un tipo de contaminación difícil de eliminar mediante reactivos químicos y generalmente solo puede eliminarse mediante limpieza desmontable;
- lodo que pasó a través de los filtros de malla – los métodos de eliminación dependen de la naturaleza del lodo.
Los intercambiadores de calor contaminados se limpian mediante lavado hidroquímico o limpieza desmontable. Se recomienda lavar cada 2-4 años, dependiendo de la calidad de los medios de trabajo.
Limpieza hidroquímica
La limpieza hidroquímica se realiza con soluciones ácidas que no afectan la superficie de las placas ni los elastómeros de sellado. La limpieza química es efectiva para intercambiadores de calor no críticamente contaminados y permite limpiar hasta el 85% de la superficie de las placas, lo cual suele ser suficiente para restaurar el funcionamiento adecuado del equipo.
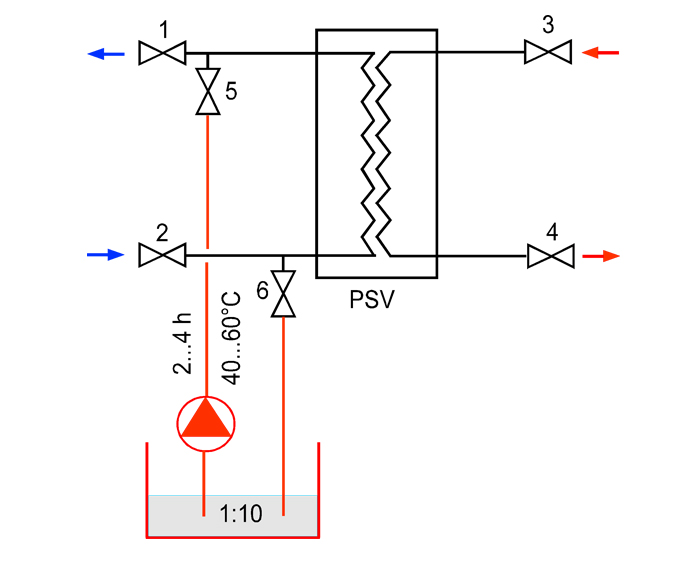
Esquema de la instalación de limpieza hidroquímica del intercambiador de calor
El lavado se realiza a través de los desagües sin desmontar el intercambiador de calor de placas ni desconectar las tuberías. La instalación de lavado consiste en una bomba de circulación y un tanque buffer para preparar y recolectar la solución ácida. Algunas versiones están equipadas con un elemento calefactor eléctrico.
Cada circuito del intercambiador de calor de placas se lava sucesivamente con una solución calentada a 40-60°C durante 2-4 horas, dependiendo del grado de contaminación del equipo. La solución se puede calentar directamente en el equipo de intercambio de calor, haciendo circular el fluido térmico en el circuito adyacente al que se está lavando.
Después de la limpieza hidroquímica, se debe enjuagar el intercambiador de calor con agua limpia hasta que el nivel de pH en la salida del equipo se estabilice.
Reactivos para la limpieza química:
- Solución de ácido clorhídrico y ácido sulfúrico - es eficaz para eliminar los depósitos de carbonato (incrustaciones), pero debido a su bajo pH=1, puede afectar negativamente el material de las placas. Se reduce la agresividad de los reactivos hacia el metal de las placas añadiendo pasivadores e inhibidores de corrosión al ácido.
- Solución de ácido cítrico orgánico - es menos eficaz en la disolución de carbonatos, pero es más amable con el material de las placas.
- Solución de ácido sulfámico - disuelve la incrustación y tiene una actividad corrosiva significativamente menor que los ácidos clorhídrico y sulfúrico. Al reaccionar con los óxidos metálicos, el ácido sulfámico forma sales (sulfamatos). Para eliminar los sulfatos, a veces se añaden compuestos de flúor a la solución.
No se recomienda lavar con:
- Adiciones que contengan cloro;
- Solución de ácido nítrico con una concentración superior al 0,5% (puede dañar las juntas de sellado).
Medidas de seguridad
La reacción química produce hidrógeno, que junto con el oxígeno forma una mezcla explosiva; ventile periódicamente el oxígeno acumulado en el intercambiador de calor durante el lavado.
Para la limpieza química del intercambiador de calor se requiere un equipo de al menos dos personas que dispongan de equipos de protección para evitar el contacto del ácido con los ojos y la piel.
El reactivo químico usado debe neutralizarse con aditivos especiales antes de ser vertido en el sistema de alcantarillado.
pregunta : comentario : opinión
345
 Catálogo de
Catálogo de Intercambiadores de Calor de Placas
Tranter
Alfa Laval
Funke
Sondex
Тепло-Поліс
Анкор-Теплоенерго
SWEP
Термопром










 Tutorial Danfoss
Tutorial Danfoss
